Veterans Affairs (VA) loans are a powerful financial tool designed specifically for veterans, active-duty service members, and eligible surviving spouses. These loans offer unique benefits that make homeownership more accessible and affordable for those who have served in the military. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down everything you need to know about VA loans, including their benefits, eligibility requirements, and how to apply.
What Are VA Loans?
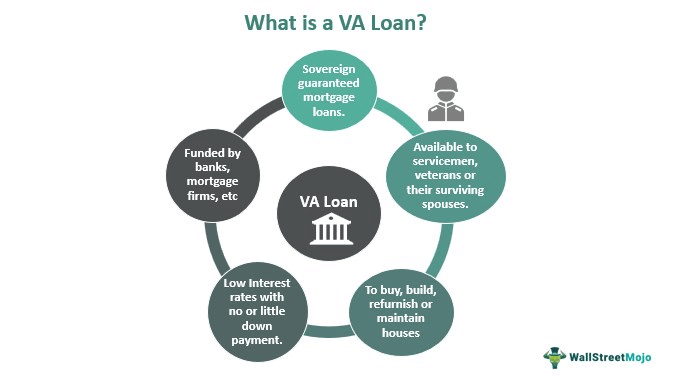
A VA loan is a type of mortgage loan guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Unlike conventional loans or FHA loans, VA loans are specifically tailored to meet the needs of veterans and service members. The program was established in 1944 as part of the GI Bill to help returning World War II veterans achieve homeownership.
Here’s how VA loans work:
- Private Lenders: While the VA guarantees a portion of the loan, private lenders such as banks or mortgage companies provide the actual financing.
- VA Guarantee: The VA’s guarantee reduces risk for lenders, enabling them to offer favorable terms like no down payment and lower interest rates.
- Purpose: These loans can be used to buy a home, build a new property, refinance an existing mortgage, or even make improvements to an existing home.
Benefits of VA Loans
VA loans come with several advantages that set them apart from other types of mortgages. These benefits are designed to make homeownership more achievable for veterans and their families.
Key Benefits:
- No Down Payment Required
- One of the most significant advantages is that VA loans typically do not require a down payment. This makes it easier for veterans to purchase homes without needing substantial upfront savings.
- No Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
- Unlike conventional loans that require PMI if you put less than 20% down, VA loans eliminate this cost entirely. This can save borrowers hundreds or even thousands of dollars annually.
- Competitive Interest Rates
- Because the VA guarantees a portion of the loan, lenders can offer lower interest rates compared to conventional mortgages.
- Flexible Credit Requirements
- While individual lenders may have credit score requirements, VA loans generally have more lenient credit standards than other types of mortgages.
- Limited Closing Costs
- The VA limits what closing costs veterans can be charged by lenders, reducing out-of-pocket expenses at closing.
- No Prepayment Penalty
- Borrowers can pay off their loan early without incurring any penalties or fees.
- Assumable Loan Option
- A VA loan can be transferred (or assumed) by another qualified borrower if you decide to sell your home.
- Foreclosure Avoidance Assistance
- The VA provides financial counseling and assistance programs to help borrowers avoid foreclosure during times of financial hardship.
- Reuse Benefit
- Eligible veterans can use their VA loan benefit multiple times throughout their lifetime as long as previous loans are paid off or entitlement is restored.
Eligibility Requirements for a VA Loan
To qualify for a VA loan, you must meet specific service-related criteria set by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility depends on your length and type of military service as well as your discharge status.
General Eligibility Criteria:
- Veterans:
- Must have served at least 90 consecutive days during wartime OR
- At least 181 consecutive days during peacetime OR
- Less than these periods if discharged due to a service-connected disability.
- Active-Duty Service Members:
- Must have served at least 90 continuous days on active duty.
- National Guard & Reserve Members:
- Must have completed at least six years in the Selected Reserve or National Guard OR
- Served at least 90 days under Title 32 orders (with at least 30 consecutive days).
- Surviving Spouses:
- Unmarried spouses of veterans who died in service or due to a service-connected disability may also qualify.
- Other Situations:
- U.S citizens who served in allied forces during World War II.
Discharge Status:
- You must not have received a dishonorable discharge.
- Certain discharges such as hardship or medical conditions may still allow eligibility upon review by the VA.
How To Apply for a Certificate of Eligibility (COE)
The first step in obtaining a VA loan is securing your Certificate of Eligibility (COE). This document proves your eligibility for the program based on your military service history.
Steps To Obtain Your COE:
- Online Through eBenefits Portal
Visit VA.gov and log into your eBenefits account to request your COE online quickly. - Through Your Lender
Most lenders can access an online system called Web LGY to retrieve your COE electronically within minutes. - By Mail
Complete Form 26-1880 (Request for Certificate of Eligibility) and mail it along with proof of military service (e.g., DD214) to your regional loan center.
Documents Needed:
- Veterans: DD214 form showing character/type of discharge.
- Active Duty Members: Statement of Service signed by commanding officer.
- National Guard/Reserve Members: NGB Form 22/23 or retirement points statement.
- Surviving Spouses: Marriage license and veteran’s death certificate (if applicable).

How To Apply For A VA Loan
Once you’ve obtained your COE, you’re ready to start applying for a VA-backed home loan through an approved lender like banks or mortgage companies.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Gather Financial Information:
- Review your credit score and debt-to-income ratio before applying.
- Prepare documents such as tax returns, pay stubs, bank statements, etc., required by lenders during underwriting.
- Choose A Lender:
- Shop around different private lenders offering competitive rates on VA-backed mortgages since terms vary between institutions.
- Get Preapproved:
- Submit necessary documentation so lenders evaluate whether they’ll approve financing based on income stability & repayment ability upfront before house hunting begins!
4 . Find Your Dream Home:
Work closely alongside real estate agents specializing helping navigate housing markets ensuring properties align budget preferences while meeting minimum property requirements outlined under VAs guidelines
5 Finalize Purchase Agreement
Finalize Purchase Agreement
Once you find a home that fits your needs and budget, the next step is to finalize the purchase agreement. This document outlines the terms of the sale, including the agreed-upon price, contingencies (such as inspections or appraisals), and closing date. Make sure to include a VA loan contingency in your agreement to protect yourself in case the property does not meet VA standards or if financing falls through.
Key Points to Remember:
- Ensure the property meets VA Minimum Property Requirements (MPRs). These requirements ensure that the home is safe, structurally sound, and sanitary.
- Work with your real estate agent to negotiate any repairs or adjustments needed before closing.
- Be prepared for an appraisal conducted by a VA-approved appraiser.
VA Appraisal Process
The VA requires an appraisal to determine the fair market value of the property and ensure it meets their MPRs. This step is crucial because it protects both you and the lender from overpaying for a home that may have significant issues.
What Happens During a VA Appraisal?
- A licensed VA appraiser evaluates the property’s condition and compares it to similar homes recently sold in the area.
- The appraiser checks for safety hazards, structural problems, and other issues that could affect livability.
- The appraised value must meet or exceed the purchase price for your loan to proceed.
If Issues Arise:
- If the appraisal comes back lower than expected, you can renegotiate with the seller or pay the difference out of pocket.
- If repairs are required to meet MPRs, work with your agent and seller to address them before closing.
Underwriting & Loan Approval
After completing the appraisal process, your lender will move forward with underwriting. During this stage, they will review all financial documents, verify your income and employment status, and assess your ability to repay the loan.
Steps in Underwriting:
- Document Verification: Lenders confirm all submitted paperwork is accurate and complete.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Your DTI ratio should ideally be below 41%, though exceptions can be made based on compensating factors like strong credit history.
- Residual Income: The VA requires borrowers to have sufficient residual income after paying monthly expenses to cover basic living costs.
Once underwriting is complete and all conditions are met, you’ll receive final loan approval!
Closing on Your VA Loan
The final step in securing your VA loan is closing day! At this point, you’ll sign all necessary paperwork to officially transfer ownership of the home into your name.
What To Expect at Closing:
- Review all documents carefully before signing anything.
- Pay any remaining closing costs (if applicable). While VA loans limit what fees veterans can be charged, some costs like prepaid taxes or homeowner’s insurance may still apply.
- Receive keys to your new home once everything is finalized!
Common Misconceptions About VA Loans
There are several myths surrounding VA loans that may discourage eligible veterans from taking advantage of this benefit. Let’s debunk some common misconceptions:
- Myth: You Can Only Use a VA Loan Once
- Fact: You can use your VA loan benefit multiple times throughout your life as long as previous loans are paid off or entitlement is restored.
- Myth: You Need Perfect Credit
- Fact: While lenders do consider credit scores during underwriting, VA loans generally have more flexible credit requirements compared to conventional mortgages.
- Myth: Only First-Time Homebuyers Qualify
- Fact: There’s no restriction on how many homes you’ve purchased previously; eligibility depends solely on military service criteria.
- Myth: Surviving Spouses Aren’t Eligible
- Fact: Unmarried surviving spouses of veterans who died in service or due to service-connected disabilities may qualify for a VA loan under certain conditions.
Tips for Maximizing Your VA Loan Benefits
To make the most out of your VA loan benefits:
- Shop around for lenders offering competitive rates since terms vary between institutions.
- Understand all associated fees upfront so there are no surprises during closing.
- Take advantage of foreclosure avoidance programs offered by the Department of Veterans Affairs if financial difficulties arise later on.
Conclusion
VA loans are one of the most valuable benefits available to veterans and active-duty service members seeking homeownership opportunities. With features like no down payment requirements, competitive interest rates, and no private mortgage insurance (PMI), these loans make buying a home more accessible than ever before. By understanding eligibility requirements and following each step carefully—from obtaining your Certificate of Eligibility (COE) through closing—you can confidently navigate this process while maximizing every advantage offered by this program.
Whether you’re purchasing your first home or refinancing an existing mortgage using a cash-out refinance option under this program—VA loans provide unmatched flexibility tailored specifically toward those who’ve served our country honorably! Don’t hesitate—start exploring today how these incredible benefits could help secure future housing needs without unnecessary financial burdens holding back dreams becoming reality sooner rather than later!
Leave a Reply